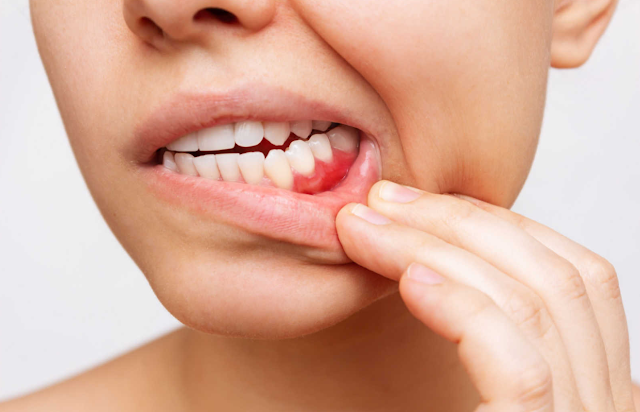
Bleeding gums can be caused by many factors, starting with something as simple as poor brushing or flossing technique. When you've finished brushing your teeth and coughed up the rest of the toothpaste, you'll see some blood. When you look in the mirror, your gums seem to bleed. Or it can also indicate an underlying medical condition.
According to MedlinePlus, the main cause of bleeding gums is plaque buildup in the gums. This can lead to a condition called gingivitis or gingivitis.
Plaque that is not removed or accumulates hardens and forms tartar. This can lead to increased bleeding and a more advanced form of gum and jaw disease called periodontal disease.
Other causes of bleeding gums can include:
- Bleeding disorders.
- Brushing teeth too hard.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
- Ill-fitting dentures or other dental appliances.
- Improper dental flossing.
- Infection, which can occur in the teeth or in the gums.
- Leukemia, a type of blood cancer.
- Skurvi, a disease caused by a deficiency of vitamin C.
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Diabetes.
Bleeding Gums home remedies
Make a habit of seeing the dentist early at least once every six months, even if you don't have any dental or oral problems. During these regular visits, your dentist can remove plaque.
Brush your teeth gently using a soft-bristled toothbrush at least twice a day, it would be even better if you brush your teeth after every meal. In addition, flossing your teeth twice a day can prevent plaque buildup and turning into tartar.
Your dentist may prescribe a salt water or hydrogen peroxide and water mouthwash, or a mouthwash specifically formulated to treat gingivitis. Some mouthwashes contain alcohol, so consult your dentist before using them.
A healthy and balanced diet can also be useful. Try to avoid snacking and limit your carbohydrate intake.
Home remedy tips that may help bleeding gums include:
- Perform a periodontal examination.
- Avoid using tobacco can make bleeding gums worse. Tobacco can also mask other problems that cause bleeding gums.
- Control bleeding gums by applying direct pressure to the gums with gauze soaked in ice water.
- If you have been diagnosed with a vitamin deficiency, take vitamin supplements as directed by your doctor.
- Avoid aspirin unless your doctor recommends taking it.
- If a medication side effect causes bleeding gums, ask your doctor to prescribe another medication. Never change medications without first talking to your doctor.
- Use an oral irrigation device on low setting to massage the gums.
- See a dentist if dentures or other dental appliances don't fit or cause painful areas of the gums.
- Follow the dentist's instructions on how to brush and floss your teeth so you don't injure your gums.
It is best to see a dentist immediately if you experience the following:
- Severe or long-term (chronic) bleeding.
- Gums continue to bleed even after being treated.
- Bleeding gums accompanied by other unexplained symptoms.
- The dentist will examine the teeth and gums in addition to asking about symptoms. The dentist will also ask about oral care habits. You may also be asked about your diet and medications used.
Other tests that may be done include:
- Blood count or blood differential test.
- X-ray of teeth and jawbone.
- Treatment from a doctor
- Bleeding Gums Should Not Be Underestimated, Here's the Reason! illustration of treatments that cause bleeding gums (pexels.com/Andrea Piacquadio)
- Treatment of bleeding gums will be adjusted to the severity, citing the National Health Service.
In the early stages, the dentist will:
- Give advice on how to keep your teeth clean, for example using an interdental brush.
- Advise to quit smoking, if you smoke.
- Suggest professional teeth cleaning.
If gum disease is serious, you may need:
- Thorough cleaning (deep cleaning) under the gums.
- Antibiotics.
- Extraction of several teeth.
- Gum surgery.
Prevention
If you see signs of gum disease, try to pay attention to your daily dental care. Described on the healthdirect page, here's how to prevent gum disease and maintain healthy gums:
- Brush your teeth after every meal, for at least two minutes.
- Use dental floss every day.
- If your gums hurt, use a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Antibacterial mouthwash can also help. Ask your dentist about this because sometimes medical mouthwashes can cause side effects.
- Dentists can also provide advice on how to care for your teeth and mouth.
- If your gums bleed regularly or worry you, make an appointment with your dentist. This could be a sign that something is wrong and requires medical intervention.
Comments
Post a Comment